The fertilizers processed by organic fertilizer production lines have various unique characteristics, which make them important in modern agricultural production. Here are some of the main characteristics of organic fertilizers:
1. Rich in organic matter
Organic fertilizers are made by the biodegradation of various organic materials such as animal manure, plant residues, compost, and green manure, and therefore contain a large amount of organic matter. The presence of organic matter can effectively improve soil structure, enhance soil water holding capacity and permeability, and create a favorable physical environment for plant growth.
2. Slowly release nutrients
Unlike quick acting chemical fertilizers, the nutrients in organic fertilizers processed by organic fertilizer production lines exist in a slow-release form. This means that nutrients will gradually be released over a longer period of time for continuous absorption by plant roots, avoiding nutrient waste and environmental risks caused by excessive one-time application.
3. Promote soil biological activity
Organic fertilizers are rich in live bacteria and enzymes, which can stimulate the reproduction and activity of beneficial microorganisms in the soil, forming an active underground ecosystem. These microorganisms participate in processes such as nitrogen fixation, phosphorus and potassium dissolution and release, helping to transform and recycle nutrients in the soil, and enhancing the soil’s self-healing ability.
4. Increase soil buffering capacity
Organic fertilizers can increase the buffering capacity of soil pH, which is the ability of soil to resist changes in acidity and alkalinity. This is crucial for maintaining a suitable acid-base balance in the soil and avoiding the impact of sudden pH changes on crop growth.
5. Improve crop quality
Crops grown with organic fertilizers typically have better flavor, color, and nutritional value. This is because the complex organic compounds in organic fertilizers can promote the production of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals in plants, making agricultural products more popular among consumers.
6. Friendly environmental protection
The environmental pollution generated during the production and use of organic fertilizers is relatively small, and it does not cause problems such as nitrate leaching and ammonia volatilization like chemical fertilizers, which helps to reduce the negative impact of agriculture on air, water sources, and ecosystems.
7. Suitable for long-term use
Due to the low but persistent nutrient content of organic fertilizers, it is not easy to cause excessive accumulation of soil nutrients, making it very suitable for long-term application on the same plot without worrying about soil degradation. This provides solid support for the development of sustainable agriculture.
8. Promote agricultural diversity
Organic fertilizers encourage the use of agricultural techniques such as crop rotation and intercropping, which help maintain field biodiversity and genetic diversity, reduce dependence on a single crop, and build a more stable and resilient agricultural production system.
In summary, the fertilizers processed by organic fertilizer production lines have shown significant advantages in promoting soil health, improving crop yield and quality, and protecting the environment due to their unique properties, making them an indispensable part of modern ecological agriculture.


.jpg)
.jpg)
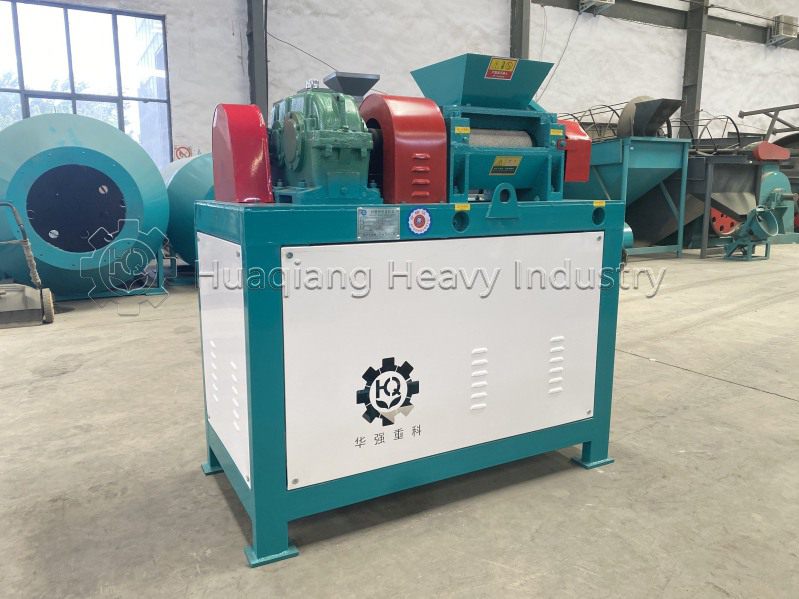
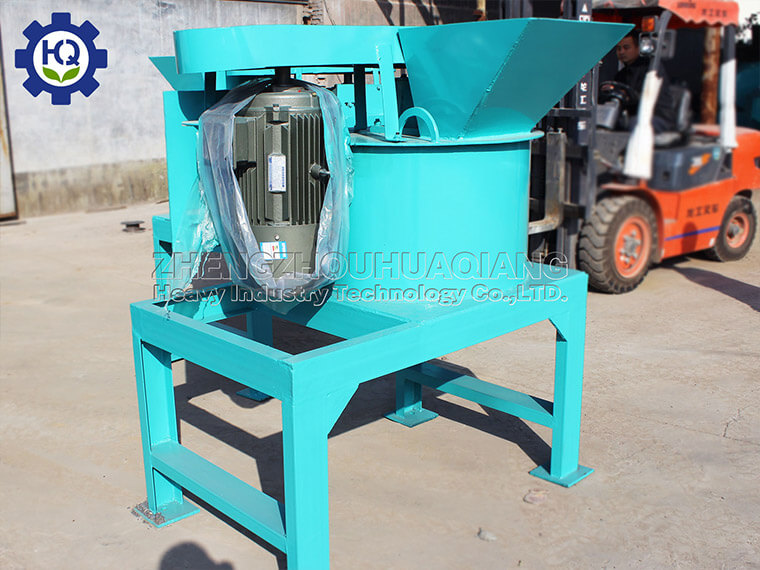
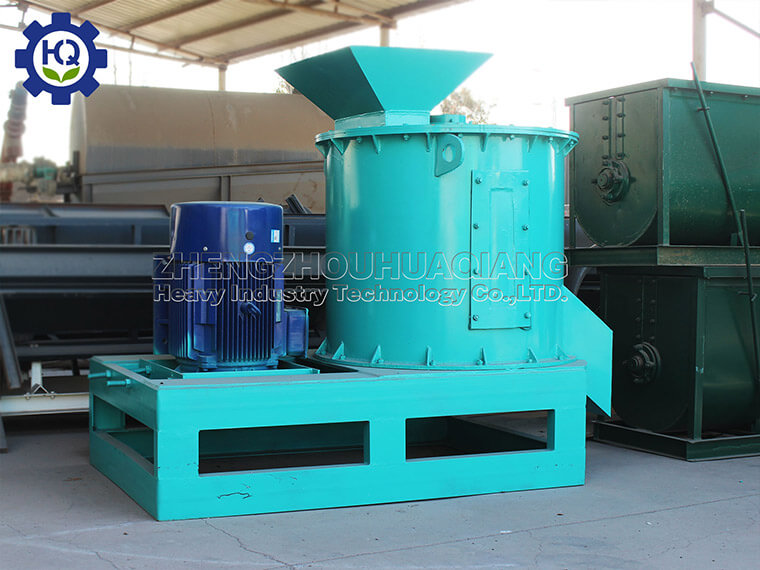



.jpg)