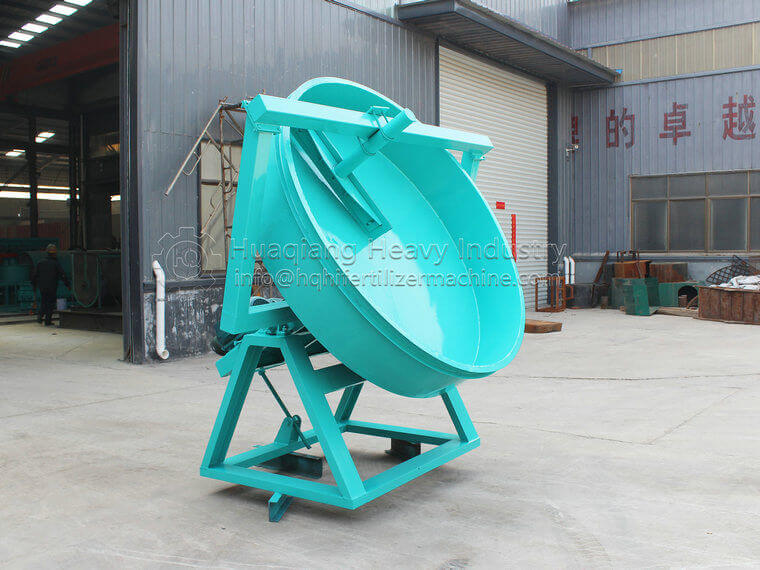
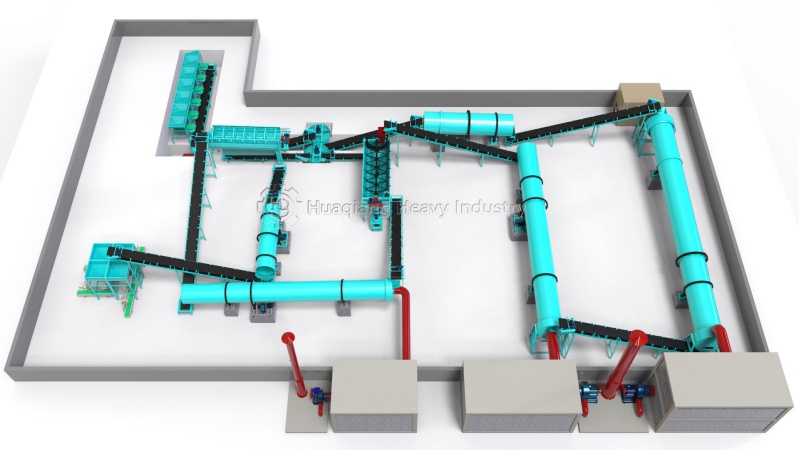
Organic fertilizer turner is a key equipment used in modern organic fertilizer production to accelerate the fermentation of organic materials such as livestock manure, crop straw, kitchen waste, etc. Its main function is to improve fermentation conditions, promote microbial activity, and accelerate the decomposition of organic matter. The following is the general workflow of an organic fertilizer turning machine:
1. Material preparation
Raw material collection and pretreatment: Collect organic materials to be fermented, crush and mix them preliminarily, and sometimes adjust the moisture content to an appropriate level (usually 40% -60%), as well as the appropriate carbon nitrogen ratio, to promote microbial activity.
2. Stacking and initial loading
Stacking: Stacking pre processed materials on a predetermined fermentation bed or fermentation tank to form a certain thickness of material pile.
3. Fermentation start-up
Intervention of flipping machine: Start the organic fertilizer flipping machine and use its unique flipping mechanism to penetrate deep into the material pile, flipping the bottom material to the surface while breaking down large clumps and ensuring uniform material distribution, increasing air circulation.
4. Ventilation and temperature control
Ventilation: The flipping process will bring fresh air into the material pile, providing the required oxygen for aerobic microorganisms and promoting rapid decomposition.
Temperature management: By flipping and adjusting the temperature inside the material pile, maintain the optimal fermentation temperature between 50 ° C and 65 ° C to accelerate the decomposition of organic matter.
5. Regularly flip the pile
Continuous flipping: According to the fermentation progress, use an organic fertilizer flipping machine to flip the entire material pile at regular intervals (such as every day or every other day) to ensure consistent fermentation effect and avoid local overheating or anaerobic conditions.
6. Monitoring and regulation
Temperature and humidity detection: Use sensors to monitor the temperature and humidity of the fermentation bed in real-time, ensuring that the fermentation process is in optimal condition.
PH and oxygen levels: Monitor pH and oxygen concentration, adjust them in a timely manner, and maintain a good fermentation environment.
7. Fermentation maturity
Maturity symbol: When the color of the material darkens, the texture becomes dry and loose, and there is no pungent odor, it indicates that fermentation has been completed.
8. Post processing
Screening and crushing: Use a screening machine to remove large pieces of undecomposed material, and then crush the fermented material into small particles through a crusher for further use or packaging.
9. Drying and Storage
Drying: Reduce the moisture content of the finished product by sun exposure or using a dryer to make it more suitable for long-term storage.
Packaging: Pack the dried organic fertilizer into bags or packages and store them in a cool and dry place for future use.
The design and use of organic fertilizer turners have greatly improved the efficiency and quality of organic fertilizer production, which is of great significance for modern agricultural production and resource recycling.




.jpg)

.jpg)