The process flow of the complete set of npk fertilizer production line equipment can usually be divided into: raw material batching, raw material mixing, raw material granulation, particle drying, particle cooling, particle classification, finished product coating, and final product packaging. The complete set of equipment has less investment, quick effect and good economic benefits. The complete set of equipment has a compact process layout, scientific and reasonable, energy saving and consumption reduction, stable operation, reliable operation and convenient maintenance. The raw material has wide adaptability and is suitable for granulation of various raw materials such as compound fertilizer, medicine, chemical industry, feed, etc. The product has a high granulation rate. Can produce various concentrations, various types including organic fertilizer, inorganic fertilizer, biological fertilizer, magnetic fertilizer and other compound fertilizers.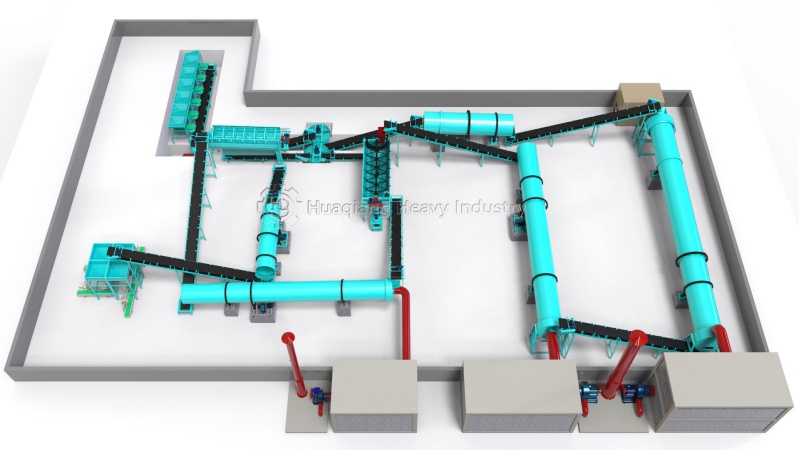
The npk manufacturing process is as follows:
1. Ingredients: urea, ammonium nitrate, ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphate (monoammonium phosphate, diammonium phosphate, heavy calcium, calcium phosphate), potassium chloride (potassium sulfate) and other raw materials in a certain proportion (according to the market demand and local soil testing results).
2. Stirring: Stir the prepared raw materials evenly to improve the overall uniform fertilizer content of the fertilizer particles.
3. Granulation: The uniformly stirred raw materials are sent to the granulator for granulation (drum granulator, extrusion granulator, double roller granulator etc).
4. Drying: The pellets made by the granulator are sent to the dryer to dry the moisture contained in the pellets to increase the strength of the pellets and facilitate storage.
5. Cooling: The temperature of the dried fertilizer granules is too high, and it is easy to agglomerate. After cooling, it is convenient for bagging, storage and transportation.
6. Screening: classify the cooled particles, re-granulate the unqualified particles, and screen out the qualified products.
7. Coating: Coating the qualified products to increase the brightness and roundness of the particles.
8. Packaging: Put the film-coated particles, that is, the finished product, in a bag and store it in a ventilated place.