The core of organic agriculture development is to balance ecological protection, agricultural product safety, and sustainable development. It’s not simply about eliminating chemical fertilizers and pesticides, but rather about following a set of scientific and systematic principles throughout the entire process to achieve harmonious coexistence between humans and nature and promote long-term agricultural development.
The primary principle is ecological priority, respecting natural laws. This involves rationally utilizing natural resources, maintaining soil through crop rotation and straw return to the field, replacing chemical control with biological control, reducing environmental pollution, and achieving sustainable ecological cycles.
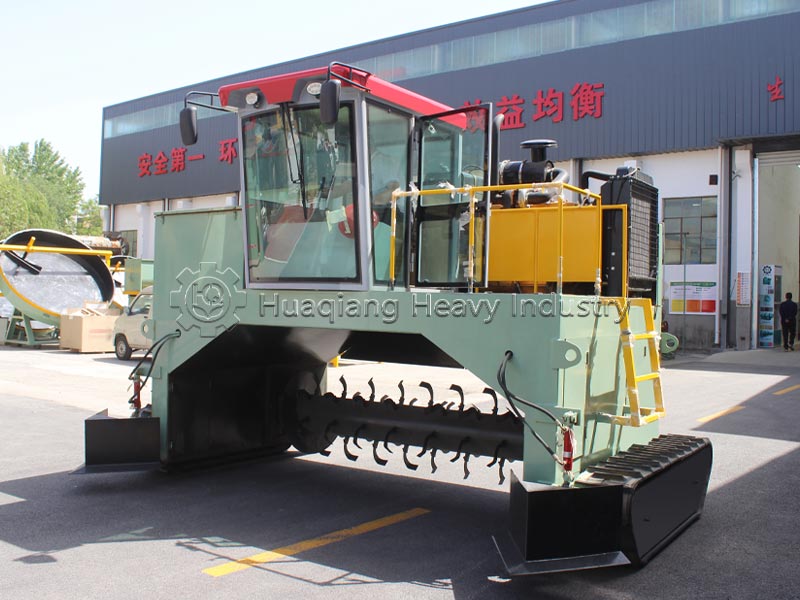
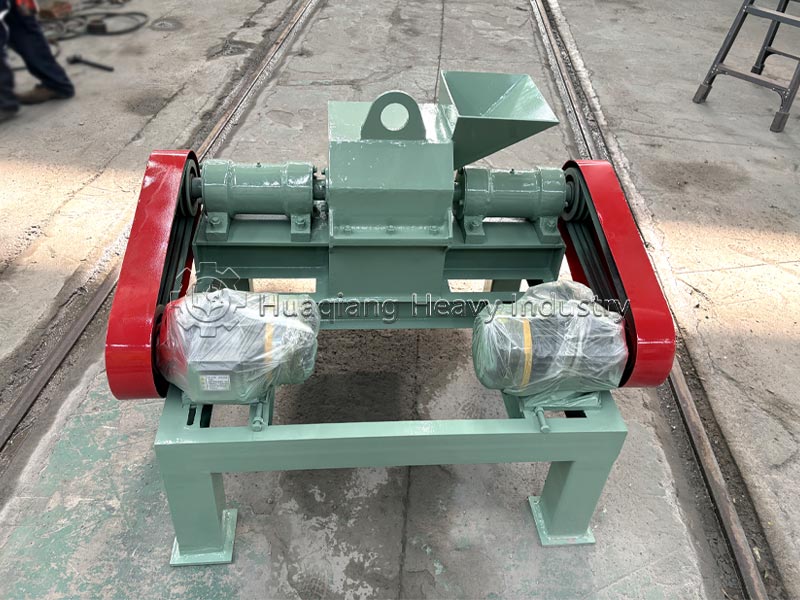
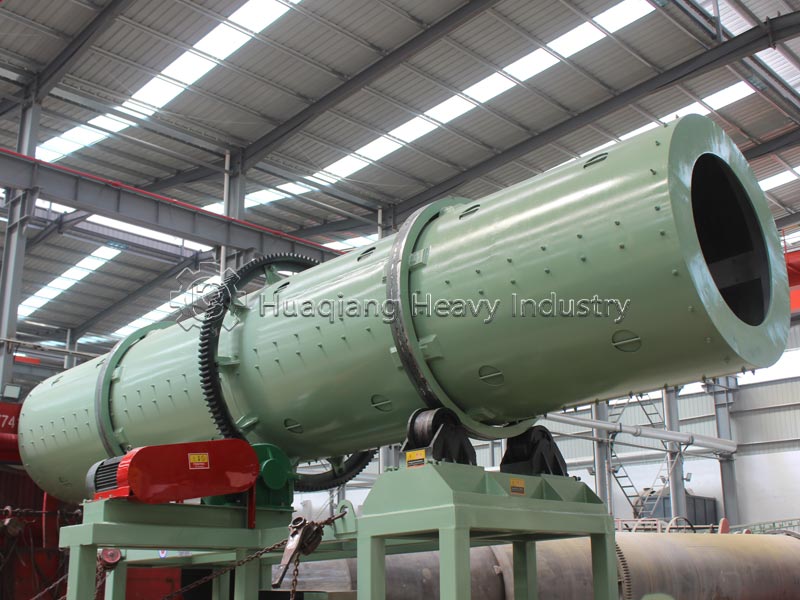
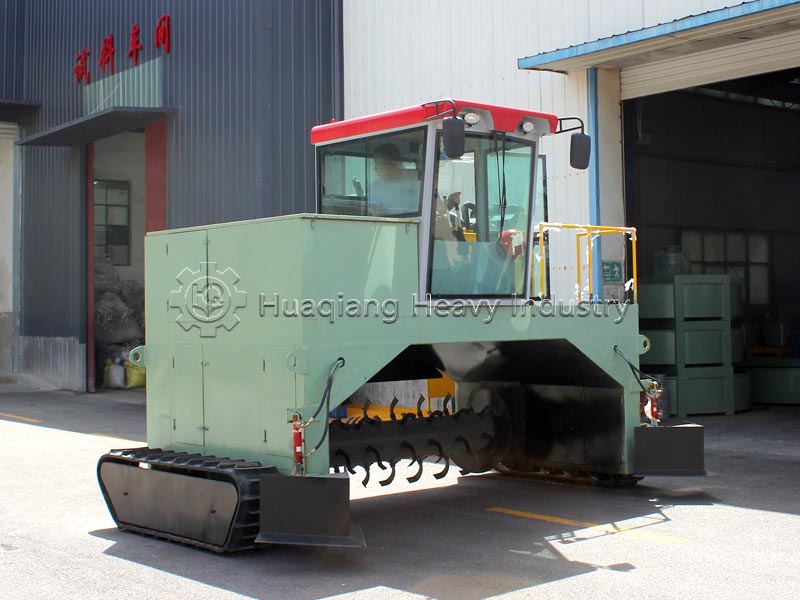
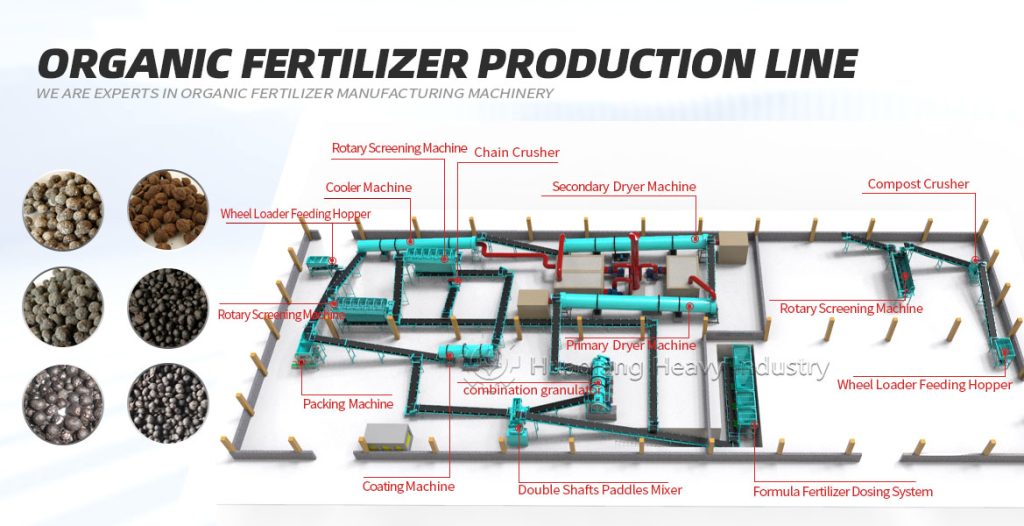
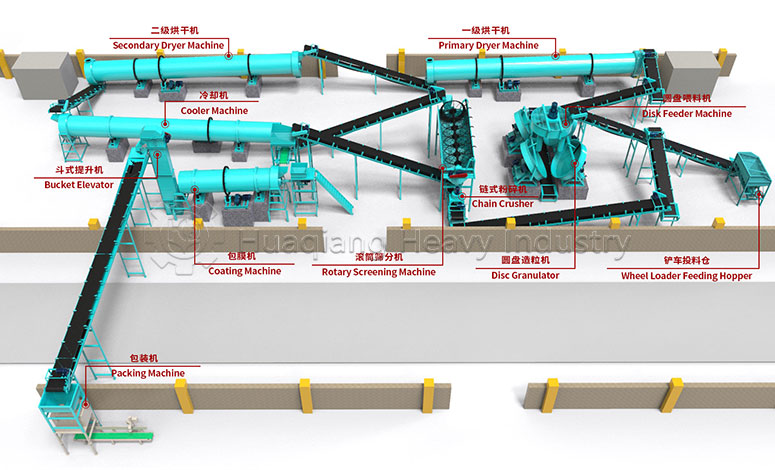
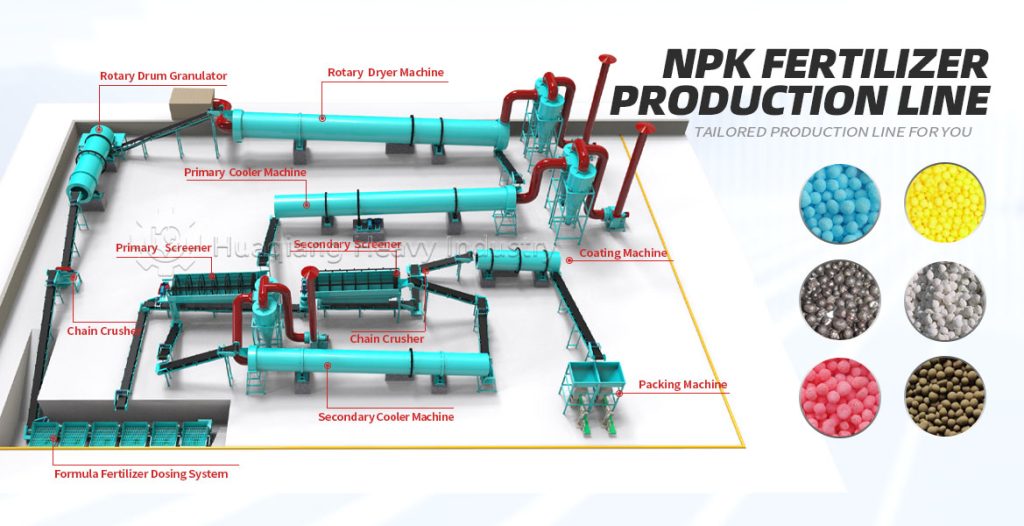
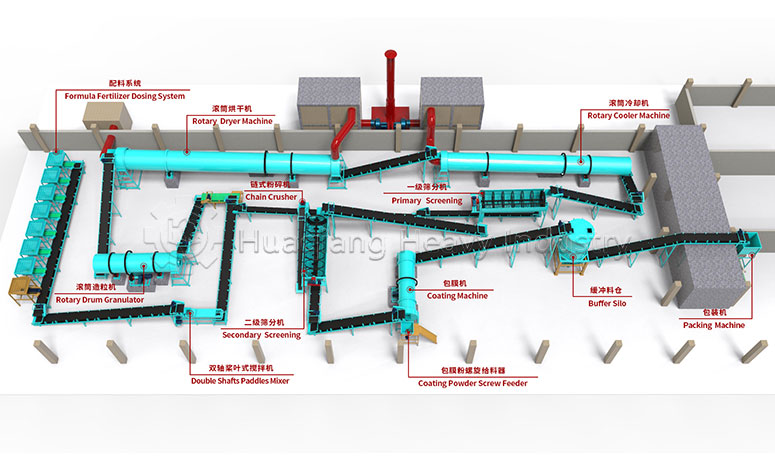
Secondly, it’s about integrating planting and animal husbandry to achieve material recycling. After harmlessly treating livestock waste, it is processed through organic fertilizer production equipment, granulated using fertilizer granulators, and then standardized on the organic fertilizer production line to produce organic fertilizer for return to the field. Simultaneously, crop straw is used to feed livestock, forming a virtuous cycle of complementary planting and animal husbandry.
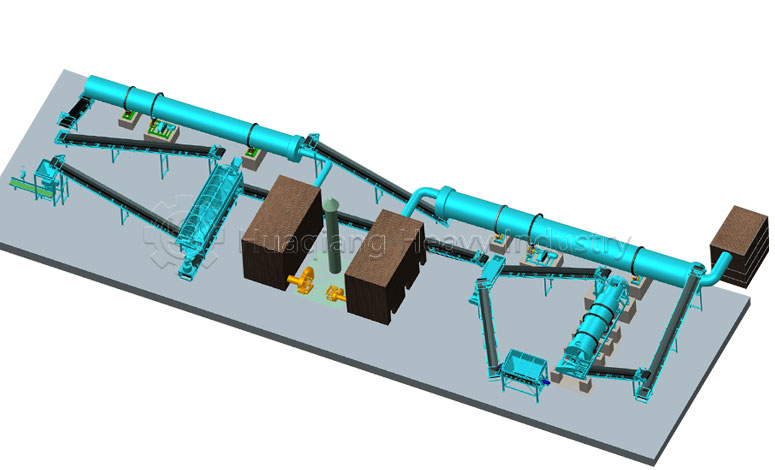
Thirdly, it’s about comprehensive control, upholding safety standards. From planting to storage and transportation, the entire process is free of synthetic chemicals. Processing relies on standardized operations using organic fertilizer production equipment and production lines, adhering to organic standards to ensure agricultural product safety.
Finally, it’s about sustainable development, balancing the present and the future. Based on the long-term conservation of agricultural resources, we must avoid over-exploitation and leave a sustainable production environment for future generations.
In summary, these four principles complement each other and are the core of high-quality development in organic agriculture. Strict adherence to them will achieve a balance of ecological, economic, and social benefits.