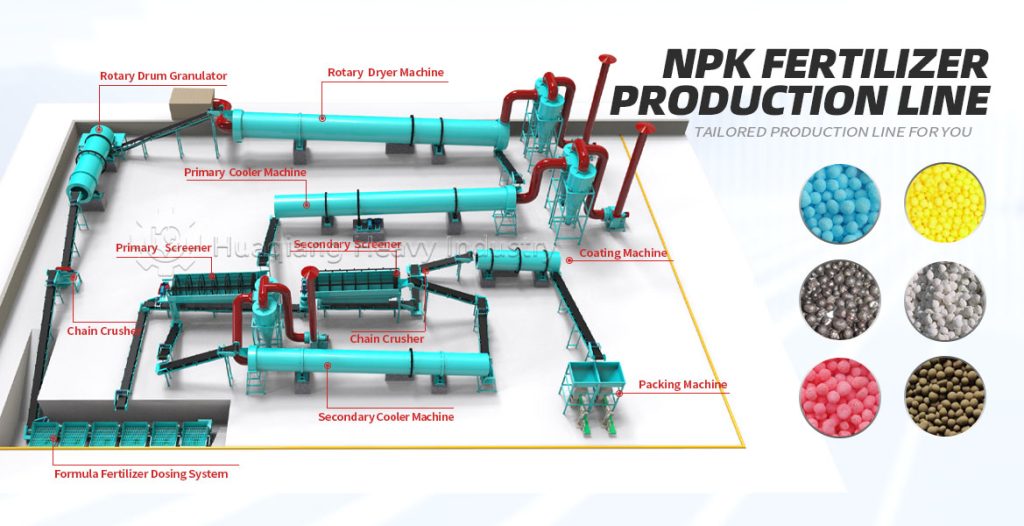
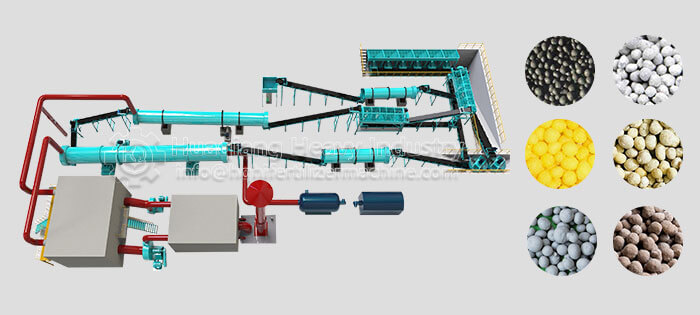
Wet granulation and dry granulation are core processes in compound fertilizer granulation. The main difference lies in whether water is added and the molding principle, adapting to different production needs. Selection should consider environmental factors, fertilizer type, and scale of production; there is no absolute superiority or inferiority between the two.
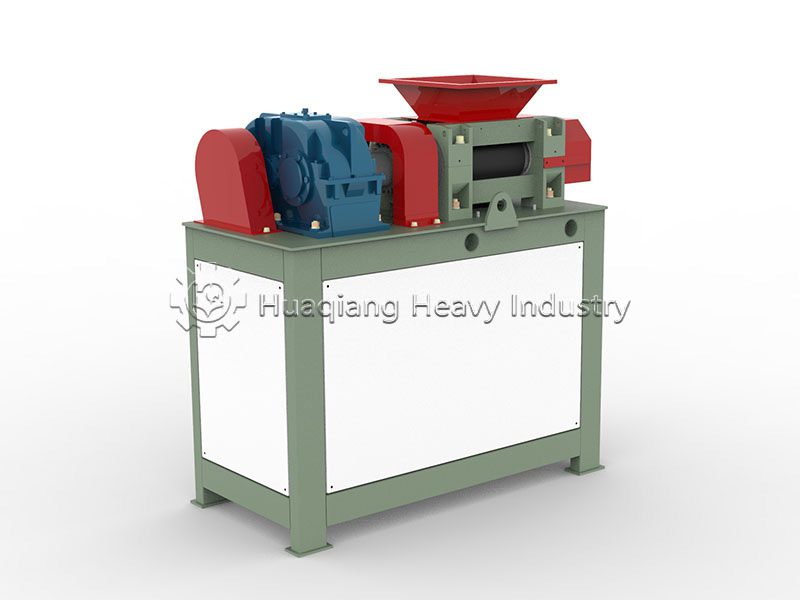
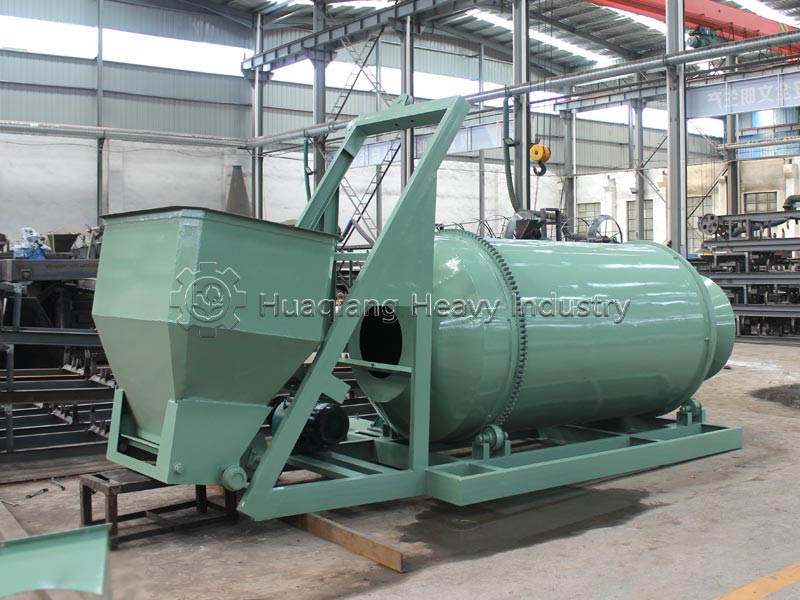
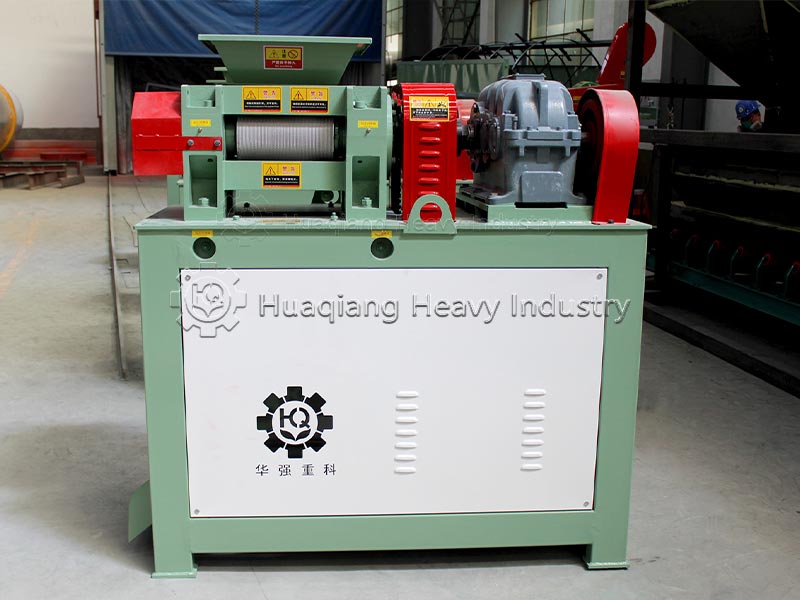
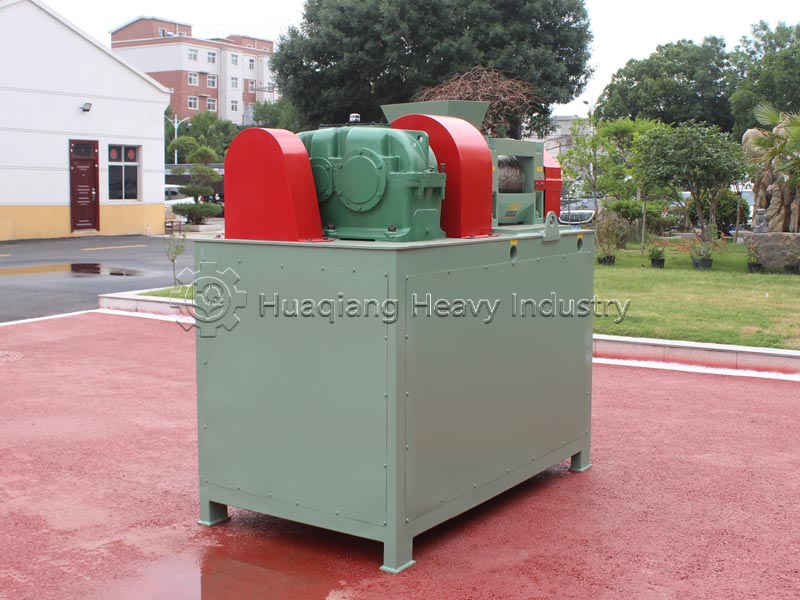
The core process and raw material suitability differ. Wet granulation of compound fertilizers requires the addition of binders and water, followed by granulation, drying, and cooling. It is suitable for low-moisture, non-caking raw materials, improving nutrient uniformity, but it can easily damage heat-sensitive components such as microbial agents. Dry granulation does not require water or drying, relying on high-pressure extrusion for molding. It is suitable for high-moisture raw materials or heat-sensitive formulations, reducing nutrient loss, and the process is simpler.

Energy consumption, environmental impact, and particle quality differ. Wet granulation requires drying equipment, resulting in high energy consumption and a small amount of wastewater that needs treatment; the granules are round and have good solubility, suitable for foliar fertilizers and drip irrigation fertilizers. Dry granulation of compound fertilizers has low energy consumption and no wastewater, meeting environmental requirements; the granules have high strength and are less prone to caking, suitable for general field fertilizers, and convenient for storage and transportation, but the regularity is slightly poorer.
The suitability for different scales of production varies significantly. Wet granulation equipment requires high investment and is suitable for large-scale continuous production, adapting to complex formula compound fertilizers. Dry granulation equipment requires moderate investment, suitable for both small-scale trial production and large-scale mass production, adapting to NPK general fertilizers and special compound fertilizers, offering greater flexibility.
In summary, choose wet granulation if you prioritize particle appearance and solubility; choose dry granulation if you prioritize environmental protection, energy saving, and nutrient retention.